



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (05): 1206-1217.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.043
樊丹1,2( ), 李涤1,2(
), 李涤1,2( ), 何登发1,2, 侯烁钦1,2, 孙天鸽1,2, 杨浩1,2, 甄宇1,2
), 何登发1,2, 侯烁钦1,2, 孙天鸽1,2, 杨浩1,2, 甄宇1,2
收稿日期:2022-03-01
修回日期:2022-06-30
出版日期:2022-10-10
发布日期:2022-11-03
通讯作者:
李涤
作者简介:李 涤,男,副教授,1984年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,从事盆地构造与大地构造研究。Email: lidi@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
FAN Dan1,2( ), LI Di1,2(
), LI Di1,2( ), HE Dengfa1,2, HOU Shuoqin1,2, SUN Tiange1,2, YANG Hao1,2, ZHEN Yu1,2
), HE Dengfa1,2, HOU Shuoqin1,2, SUN Tiange1,2, YANG Hao1,2, ZHEN Yu1,2
Received:2022-03-01
Revised:2022-06-30
Online:2022-10-10
Published:2022-11-03
Contact:
LI Di
摘要:
东天山博格达地区经历了古生代长期俯冲增生与中—新生代多期陆内变形改造作用,但对于博格达山石炭纪构造属性与演化阶段等问题始终存在争议,制约了对北疆晚古生代构造格局的认识。利用博格达山露头及其两侧盆地钻井、地震资料,运用盆地构造分析思路与方法从盆-山尺度开展了石炭系地层格架及岩浆活动特征综合对比研究,划分博格达地区石炭系构造-地层单元并分析石炭纪构造背景。研究结果显示:博格达山相邻的准噶尔盆地和吐哈盆地发育下石炭统与下伏地层(C1/AnC)不整合,而上、下石炭统之间(C2/C1)、二叠系与上石炭统(P/C2)不整合在博格达山及相邻盆地普遍存在,由此将博格达地区石炭系划分为下石炭统和上石炭统2个主要构造层,揭示研究区经历了两个主要的构造演化阶段。进一步结合构造变形演化、盆地构造沉降特征及构造环境分析结果,认为博格达山石炭纪为俯冲相关伸展背景下的弧后盆地,经历了早、晚石炭世两阶段伸展裂陷作用,并在裂陷晚期均明显遭受了周缘块体碰撞拼贴事件的影响。
中图分类号:
樊丹, 李涤, 何登发, 侯烁钦, 孙天鸽, 杨浩, 甄宇. 东天山博格达地区石炭系构造-地层划分及成盆背景分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(05): 1206-1217.
FAN Dan, LI Di, HE Dengfa, HOU Shuoqin, SUN Tiange, YANG Hao, ZHEN Yu. Carboniferous Tectono-stratigraphic Division and Basin-forming Background in the Bogda Area, Eastern Tianshan[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(05): 1206-1217.

图1 中亚造山带构造纲要图[8,23](a)和东天山地区主要构造单元[8](b)(岩浆岩年龄数据来自文献[8]及其统计结果)
Fig.1 Tectonic outline of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[8,23] (a) and major tectonic units in the East Tianshan area[8](b)(age data of the magmatic rocks from ref.[8])

图5 准噶尔盆地城1井石炭系地层序列(a)及过城1井地震-地质结构剖面特征(b) AnC.前石炭系;C1sj.下石炭统双井子组;C2b.上石炭统巴塔玛依内山组;C2sh.上石炭统石钱滩组;P.二叠系;J.侏罗系;N.第三系
Fig. 5 Carboniferous stratigraphic sequence of the Well Cheng1 in the Junggar Basin(a) and Well Cheng1-related seismic geological structure profile(b)
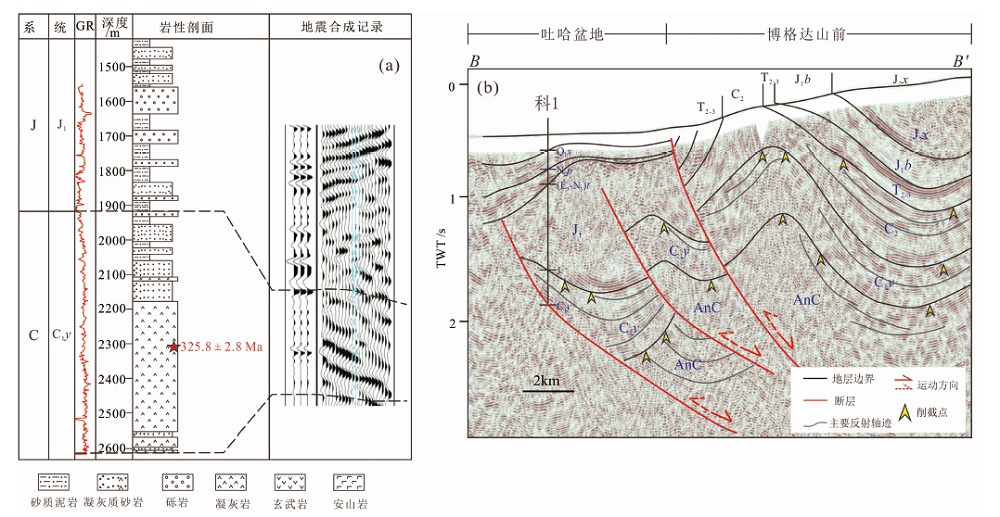
图6 吐哈盆地科1井石炭系地层序列(a)及过科1井地震-地质结构剖面特征(b) AnC.前石炭系;C1y.下石炭统雅满苏组;C2.上石炭统;T2-3.中-上三叠统;J1.下侏罗统;J1b.下侏罗统八道湾组;J1x.下侏罗统西山窑组
Fig. 6 Carboniferous stratigraphic sequence of the Well Ke1 in the Tuha Basin(a) and Well Ke1-related seismic geological structure profile(b)

图8 不同成因类型盆地构造沉降曲线特征[49](a)和博格达地区石炭纪盆地构造沉降曲线特征(b)
Fig.8 Characteristics of tectonic subsidence in the different mechanisms basins[49] (a) and characteristics of Carboniferous tectonic subsidence in the Bogda area(b)
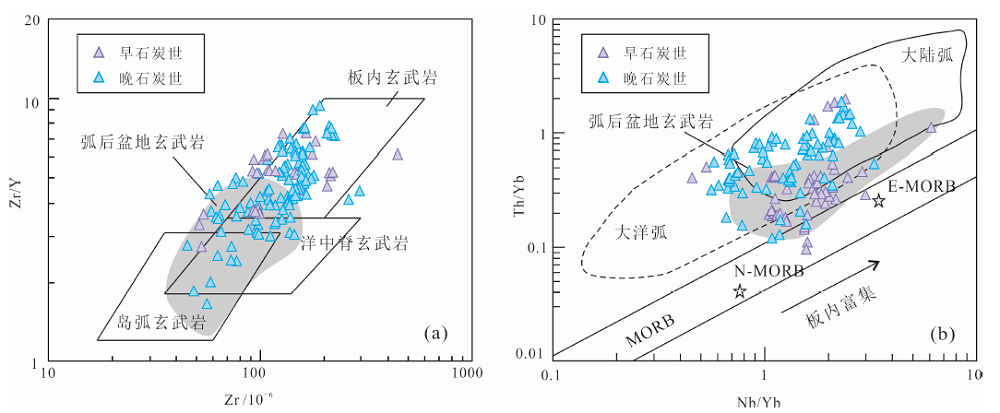
图9 博格达山石炭纪岩浆岩构造环境判别图解 (a)Zr/Y-Zr图解;(b)Th/Yb-Nb/Yb图解;石炭纪岩浆岩年龄数据及微量元素来自文献[8]及其统计结果;MORB.洋中脊玄武岩;N-MORB.正常型洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB.富集型洋中脊玄武岩
Fig.9 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Carboniferous magmatic rocks
| [1] |
WINDLEY B F, ALEXEIEV D, XIAO W J, et al. Tectonic mo-dels for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164: 31-47.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HUANG B, FU D, KUSKY T, et al. Sedimentary provenance in response to Carboniferous arc-basin evolution of East Junggar and North Tianshan belts in the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 722: 324-341.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHANG Y Y, PE-PIPER G, PIPER D J W, et al. Early Carboniferous collision of the Kalamaili orogenic belt, North Xinjiang, and its implications: Evidence from molasse deposits[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2013, 125(5/6): 932-944.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 舒良树, 卢华复, 印栋浩, 等. 新疆北部古生代大陆增生构造[J]. 新疆地质, 2001, 19(1): 59-63. |
| [5] | 肖文交, 舒良树, 高俊, 等. 中亚造山带大陆动力学过程与成矿作用[J]. 新疆地质, 2008, 26(1): 4-8. |
| [6] |
CHEN X J, SHU L S, SANTOSH M, et al. Island arc-type bimodal magmatism in the eastern Tianshan Belt, Northwest China: Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and implications for the Paleozoic crustal evolution in Central Asia[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168/169: 48-66.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MEMTIMIN M, PE-PIPER G, PIPER D J W, et al. Carboniferous arc-related volcanism in SW Bogda Mountain, Northwest China, and its implications for regional tectonics[J]. Lithos, 2020, 360/361: 105413.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI D, HE D F, LU Y, et al. Diverse origins of Late Paleozoic calc-alkaline magmatic rocks from the Bogda tectonic belt: Implications for the geodynamic evolution of the eastern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Lithos, 2021, 404/405: 106442.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
XIAO W J, ZHANG L C, QIN K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China): Implications for the continental growth of Central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4): 370-395.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CHEN K, LIN W, WANG Q. The Bogeda Shan uplifting: Evidence from multiple phases of deformation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 99: 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 王宗秀, 李涛, 周高志, 等. 博格达山晚石炭纪造山活动的变形地质记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(1): 63-69. |
| [12] |
COLEMAN R G. Continental growth of northwest China[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8(3): 621-635.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
XIE W, LUO Z Y, XU Y G, et al. Petrogenesis and geochemistry of the Late Carboniferous rear-arc (or back-arc) pillow basaltic lava in the Bogda Mountains, Chinese North Tianshan[J]. Lithos, 2016, 244: 30-42.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 马瑞士. 东天山构造演化与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997. |
| [15] |
SHU L S, WANG B, ZHU W, et al. Timing of initiation of extension in the Tianshan, based on structural, geochemical and geo-chronological analyses of bimodal volcanism and olistostrome in the Bogda Shan (NW China)[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2011, 100(7): 1647-1663.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WALI G, WANG B, CLUZEL D, et al. Carboniferous-Early Permian magmatic evolution of the Bogda Range (Xinjiang, NW China): Implications for the Late Paleozoic accretionary tectonics of the SW Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 153: 238-251.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG Y Y, YUAN C, LONG X, et al. Carboniferous bimodal volcanic rocks in the Eastern Tianshan, NW China: Evidence for arc rifting[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 43: 92-106.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 夏林圻, 张国伟, 夏祖春, 等. 天山古生代洋盆开启、闭合时限的岩石学约束--来自震旦纪、石炭纪火山岩的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(2): 55-62. |
| [19] | 何国琦, 李茂松, 刘德权, 等. 中国新疆古生代地壳演化及成矿[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆人民出版社, 1994. |
| [20] | 顾连兴, 胡受奚, 于春水, 等. 论博格达俯冲撕裂型裂谷的形成与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(4): 585-597. |
| [21] | 王银喜, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 等. 博格达裂谷双峰式火山岩地质年代学与Nd-Sr-Pb同位素地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5): 1215-1224. |
| [22] | 易鹏飞. 东天山博格达-巴里坤塔格石炭纪-早二叠世陆内裂谷演化特征[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2013. |
| [23] | WANG J L, WU C, LI Z, et al. The Pennsylvanian composite volcanism in the Bogda Mountains, NW China: Evidence for pstcollisional rift basins[J]. Lithosphere, 2020(1): 1-22. |
| [24] | 孙国智. 新疆博格达地区石炭纪原型盆地分析[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2009. |
| [25] | 赵同阳, 徐仕琪, 朱志新, 等. 新疆博格达-哈尔里克山地区石炭纪火山岩地质地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(1): 115-124. |
| [26] | 李锦轶, 何国琦, 徐新, 等. 新疆北部及邻区地壳构造格架及其形成过程的初步探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(1): 148-168. |
| [27] | 徐学义, 李向民, 马中平, 等. 北天山巴音沟蛇绿岩形成于早石炭世:来自辉长岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(8): 1168-1176. |
| [28] | 徐学义, 马中平, 夏林圻, 等. 北天山巴音沟蛇绿岩斜长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP测年及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2005, 51(5): 45-49. |
| [29] | 秦彪. 阿勒吞昆多蛇绿混杂岩斜长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP测年及时限[J]. 西北地质, 2012, 45(3): 20-25. |
| [30] |
HAN B F, GUO Z J, ZHANG Z C, et al. Age, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of a Late Paleozoic stitching pluton in the North Tian Shan suture zone, western China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010, 122(3/4): 627-640.
DOI URL |
| [31] | LI D, HE D F, SUN M, et al. The role of arc-arc collision in accretionary orogenesis: insights from -320 Ma tectono-sedimentary transition in the Karamaili Area, NW China[J]. Tectonics, 2020, 39(1): 1-21. |
| [32] | 吴友平. 博格达山北缘构造变形及构造演化特征[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2019. |
| [33] | 熊发挥, 杨经绥, 贾毅, 等. 新疆博格达白杨沟的枕状熔岩:岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素特征[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(4): 838-854. |
| [34] | 汪晓伟. 东天山博格达东段晚古生代火山岩岩石学、地球化学及其构造属性[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016. |
| [35] | 赵斐宇. 吐哈盆地石炭系-二叠系地层厚度及火山岩分布特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015. |
| [36] | 王银喜, 顾连兴, 张遵忠, 等. 东天山晚石炭世大石头群流纹岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(7): 1749-1755. |
| [37] |
XIE W, XU Y G, CHEN Y B, et al. High-alumina basalts from the Bogda Mountains suggest an arc setting for Chinese Northern Tianshan during the Late Carboniferous[J]. Lithos, 2016, 256/257: 165-181.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 张妍, 李振生, 聂峰, 等. 新疆博格达山晚古生代地层的形成时代、物源及其演化:碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学证据[J]. 地质科学, 2015, 50(1): 155-181. |
| [39] |
ZHANG Y Y, YUAN C, SUN M, et al. Two Late Carboniferous belts of Nb-enriched mafic magmatism in the Eastern Tianshan: Heterogeneous mantle sources and geodynamic implications[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2020, 132(9/10): 1863-1880.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 李涤. 准噶尔盆地及邻区石炭纪构造格架与沉积充填演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [41] | 苏春乾, 姜常义, 夏明哲, 等. 北天山东段阿奇山组火山岩的地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(4): 901-915. |
| [42] | 汪晓伟, 崔方磊, 孙吉明, 等. 博格达造山带东段芨芨台子地区早二叠世双峰式火山岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(4): 100-114. |
| [43] |
CHEN X, SHU L S, SANTOSH M. Late Paleozoic post-collisional magmatism in the Eastern Tianshan Belt, Northwest China: New insights from geochemistry, geochronology and petrology of bimodal volcanic rocks[J]. Lithos, 2011, 127(3/4): 581-98.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 高景刚, 李文渊, 周义, 等. 新疆博格达东缘色皮口地区柳树沟组流纹岩地球化学、LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2013, 49(4): 665-675. |
| [45] | 汪晓伟, 徐学义, 马中平, 等. 博格达造山带东段萨尔乔克地区早石炭世双峰式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 58-70. |
| [46] | 施文翔, 田少亭, 冯红刚, 等. 东天山博格达造山带黑沟环状花岗杂岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及地质意义[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015, 35(2): 251-256. |
| [47] |
ZHANG X B, CHAI F M, CHEN C, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic implications of Late Carboniferous Daheyan intrusions from the Bogda Mountains, eastern Tianshan[J]. Geological Magazine, 2019, 157(2): 289-306.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 卢苗安. 天山东段盆山构造格局的多期演变[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2007. |
| [49] | ALLEN P A, ALLEN, J R. Basin Analysis: Principles and Application to Petroleum Play Assessment[M]. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2013: 1-642. |
| [50] | 张磊. 准噶尔地区石炭纪盆地地质结构、充填及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [51] | 孙天鸽. 吐哈盆地石炭-二叠系构造-地层层序与沉积充填演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2022. |
| [1] | 陈俊, 王剑, 雷海艳, 马聪, 孟颖, 齐婧. 火成岩风化壳储集层特征与油气产能关系研究:以准噶尔盆地红山嘴石炭系油藏为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1009-1021. |
| [2] | 辛云路, 王劲铸, 金春爽. 南盘江盆地石炭系沉积体系及页岩气有利区带[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 774-785. |
| [3] | 范存辉, 吴强, 邓玉森, 李虎, 韩雨恬. 火山岩风化壳储层特征及分布规律——以准噶尔西北缘中拐凸起石炭系火山岩为例[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(05): 1046-1058. |
| [4] | 伊硕, 黄文辉, 金振奎, 高白水, 朱小二. 哈萨克斯坦Zanazor油田石炭系KT-Ⅱ碳酸盐岩层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 791-801. |
| [5] | 冯兴雷,付修根,谭富文,陈文彬. 羌塘盆地孔孔茶卡地区石炭系擦蒙组烃源岩沉积环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(5): 953-961. |
| [6] | 吴康军,刘洛夫,曾丽媛,白振华. 准噶尔盆地车排子周缘白垩系底部不整合面的形成及其油气输导作用[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1153-1160. |
| [7] | 张明峰, 妥进才, 张小军, 邱军利, 吴陈君, 郭力军, 嵇文涛. 柴达木盆地北缘东段石炭系生烃潜力及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 723-731. |
| [8] | 林晓英, 曾溅辉, 杨海军, 张宝收, 曲正阳. 塔里木盆地哈得逊油田石炭系地层水化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2): 377-383. |
| [9] | 左国朝, 刘义科, 张招崇, 黄河. 中亚地区中、南天山造山带构造演化及成矿背景分析[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(1): 1-14. |
| [10] | 李儒峰, 柳广弟, 马国富, 高岗, 方晶, 刘玉娥. 武威盆地石炭系层序地层学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(6): 1048-1056. |
| [11] | 张舒, 张招崇, 黄河, 张东阳, 薛春纪. 南天山沙里塔什铅锌矿床地质特征及S、Pb同位素特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(5): 856-865. |
| [12] | 陈庆 张立新. 准噶尔盆地西北缘石炭系火山岩岩性岩相特征与裂缝分布关系[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 305-312. |
| [13] | 吴晓智,齐雪峰,唐勇,卫延召,侯连华. 新疆北部石炭纪地层、岩相古地理与烃源岩[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(4): 549-557. |
| [14] | 顾雪祥,董树义,王银宏,胡贵增,杜树浩,焦鹏. 不整合面控制内生金属成矿的新实例:山东沂南金铜铁矿床[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 151-161. |
| [15] | 郑宽兵. 邓军. 李浩. 冯彩琴. 唐晓川.. 滇黔桂盆地及其邻区二叠系与三叠系之交的淹没不整合面[J]. 现代地质, 2004, 18(4): 564-571. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||